
Can India Lead the Way in Developing Climate-Resilient Crops?
Can India Lead the Way in Developing Climate-Resilient Crops? India, a nation heavily reliant on agriculture, faces a critical challenge:

Can India Lead the Way in Developing Climate-Resilient Crops? India, a nation heavily reliant on agriculture, faces a critical challenge:

The Impact of Climate Change on India’s Agricultural Sector The Looming Threat: Climate Change and its Impact on India’s Agricultural

Wildlife Conservation in India: Balancing Development with Nature Wildlife Conservation in India: Balancing Development with NatureIndia, a land of vibrant

India’s Efforts to Combat Deforestation: Are They Enough? India, a land of diverse landscapes, boasts rich biodiversity within its forests.

Air Pollution Concerns: Can India Breathe Easy Again? Air Pollution Concerns: Can India Breathe Easy Again? India, a land of
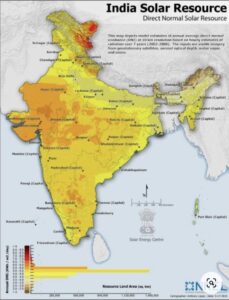
India’s Ambitious Renewable Energy Target: Can It Be Achieved? India, the world’s second-most populous nation, faces a monumental challenge: balancing

India, the world’s second-most populous country, is witnessing a surge in electric vehicle (EV) adoption. Driven by government incentives, environmental

The world is hurtling towards a clean energy future, and at the heart of this transformation lies battery technology. From

India, the world’s third-largest energy consumer, is grappling with a two-fold challenge: ensuring energy security and transitioning towards a cleaner

From Trash to Treasure: India’s Innovative Recycling & Upcycling Initiatives From Trash to Treasure: India’s Innovative Recycling & Upcycling InitiativesIndia,