The growing demand for electric vehicles and portable electronics has led to a significant increase in the production of lithium-ion batteries. However, the disposal of used lithium batteries poses a serious environmental threat due to their potential to release hazardous materials into the environment. Recycling of lithium batteries is therefore becoming increasingly important, and there is ongoing research in the United States and other countries on how to improve this process.
Lithium batteries contain a variety of materials, including lithium, cobalt, nickel, and graphite. When these batteries are not properly disposed of, they can release toxic chemicals into the environment, including lead, mercury, and cadmium. The improper disposal of lithium batteries can also lead to fires and explosions, causing further environmental damage.
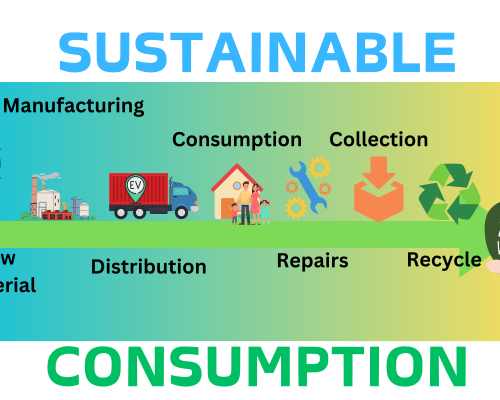
In recent years, there has been a significant increase in the recycling of lithium batteries. The recycling process typically involves crushing the batteries and then separating the valuable materials, such as cobalt, nickel, and lithium, from the less valuable ones. These materials can then be used to manufacture new batteries, reducing the demand for new materials.
In the United States, there has been a significant effort to improve the recycling of lithium batteries. The Department of Energy’s Vehicle Technologies Office has been investing in research to develop new recycling technologies, including hydrometallurgical processes that can recover materials more efficiently than traditional methods.
Several companies are also working on developing new recycling technologies. For example, Li-Cycle, a Canadian company, has developed a process that can recover up to 95% of the materials in lithium batteries. The company uses a combination of mechanical and chemical processes to break down the batteries and recover the valuable materials.
In Europe, the European Union has set a target of recycling 55% of all lithium batteries by 2025. The EU has also established regulations on the disposal of lithium batteries, requiring manufacturers to take responsibility for the proper disposal of their products.
China, which is the largest producer of lithium-ion batteries, has also been investing in research on recycling. The country has established a number of research centers dedicated to developing new recycling technologies, and several companies are already offering recycling services.
Overall, the recycling of lithium batteries is becoming increasingly important as the demand for electric vehicles and portable electronics continues to grow. While there are challenges to overcome, ongoing research and development are providing new solutions to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of the recycling process. By recycling lithium batteries, we can reduce the environmental impact of these products and ensure that valuable materials are not wasted.